What is Proof of Stake (PoS)? New Premier Guide 2024
Compared to standard databases with central authority, blockchain is a peer-to-peer decentralized network where anyone can participate. Classic blockchain systems are built on cryptography and form a sequential chain of data blocks written one after another. They have certain fundamental properties, depending on how they are written into the blockchain.
To make the system function properly and considering that blockchain nodes are independent of each other, each node must adhere to specific (but uniform) rules to validate blockchain transactions and write blocks into the chain. This set of rules is known as the blockchain consensus algorithm.
In this article, we will explore the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, its advantages and disadvantages, and how it differs from another equally popular consensus algorithm known as Proof of Work. Finally, you will learn about some blockchain projects based on the PoS algorithm.
What is PoS consensus algorithm and how does it work?
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an algorithm used to validate ownership of digital currency within a total pool of shares. PoS consensus algorithm is the second most popular algorithm implemented in cryptocurrencies. As an idea, the Proof of Stake algorithm was proposed on the Bitcointalk forum in 2011, and the cryptocurrency PeerCoin first implemented the protocol in 2012.
The algorithm requires network participants – cryptocurrency owners. They join groups and delegate their token mining rights to a participant who forms a pool of participants for all delegates. Such network nodes are called validators.
The Proof of Stake system was created as an alternative to Proof of Work, aiming to overcome its drawbacks such as massive computational power consumption. This mechanism reduces the computational work required to validate transactions and protect blocks of distributed ledger. The PoS method essentially substitutes processing power with stake, where the network determines an individual’s mining capability. Owners stake their tokens to gain the ability to validate new blocks and become “validators.”
Validators carry out the process of validating transactions, ensuring the correctness of transactions within blocks. If the operation is correct, they add the block to the blockchain and receive rewards for their contribution. However, if validators propose adding a block with intentionally incorrect data, they will lose some staked assets as a penalty.
In PoS algorithm, all coins can be pre-generated and then distributed among network members. There are various implementations of PoS blockchain consensus mechanisms, listed as follows PoS systems:
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
This algorithm differs from the classic distributed ledger consensus system PoS mainly in an attempt to overcome the main drawback of the algorithm, namely the risk of centralization. In DPoS, the right to approve cryptocurrency transactions is delegated by token holders to validators, who are voted in by the holders.
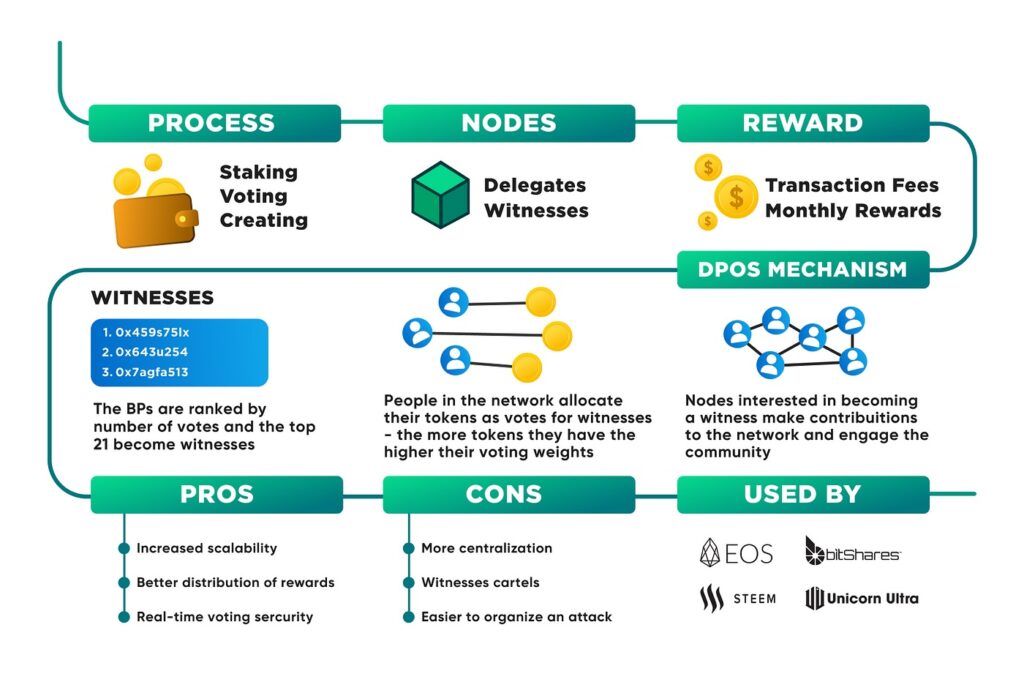
Any network member who owns a certain amount of cryptocurrency can become a validator. Nevertheless, at any time, votes for that validator can be withdrawn to support another validator. However, DPoS also has drawbacks. Specifically, the risk is low participation of network participants, after which DPoS turns into PoS, and collusion by representatives cannot be ruled out.
Leased Proof of Stake (LPoS)
This type of PoS involves leased ownership proof shares. It is a pool of network participants who lease their shares to participants with a large amount of cryptocurrency, forming a node. Due to the leased cryptocurrency, network participants have the opportunity to earn their share of cryptocurrency from mining nodes; otherwise, the chance of receiving rewards is small due to the small share of network participants in the entire market for a given cryptocurrency.
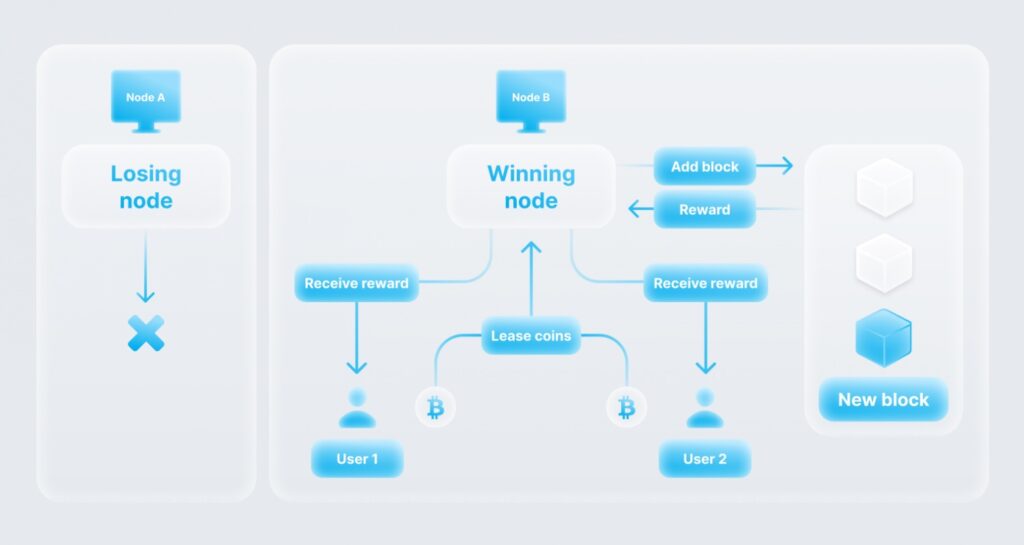
The process of mining cryptocurrencies based on PoS consensus is called forging. It involves creating a master node running on a dedicated computer that is usually always connected to the Internet. The dedicated computer runs a cryptocurrency wallet with the least amount of cryptocurrency. It is only profitable for master nodes to operate using cryptocurrencies with a negligible low popularity value. If their value increases, you can become a large owner and operate your master node.
Key Points
- Proof of Stake is a protocol for adding new blocks and validating transactions.
- PoS is more environmentally friendly and faster, but it tends to be centralized – whoever owns a critical amount of tokens can control the network.
- PoS systems were created as an alternative to Proof of Work, aiming to overcome its drawbacks such as massive power consumption.
Pros and Cons of Proof of Stake (PoS) Algorithm
As cryptographic technologies develop, more and more different consensus algorithms emerge, each of which must be better than the previous one to drive the development of blockchain networks. Proof of Stake, as one of the most popular consensus mechanisms today, has its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of Proof of Stake (PoS) Algorithm
This consensus algorithm has many impressive advantages.
1. Eco-Friendliness
The sustainability of cryptographic technology is a sharp issue, as the processes of mining new currencies and maintaining other important processes of the blockchain system (including various consensus algorithms, one of which is PoS) consume a lot of energy. Unlike other types of algorithms, PoS is an energy-efficient algorithm that does not require high consumption due to the optimization of the mathematical models on which the consensus mechanism operates. This makes it possible to reduce energy consumption and significantly reduce the environmental impact of the mining process.
2. High Security Level
A 51% attack is an attack on a blockchain network. It is characterized by one person, group, or organization gaining control of the majority of the hash rate (hashing power) of the network. In this case, the attacker would have the power to reorder or delete transactions. For example, deleting transactions allows the attacker to double spend cryptocurrencies. The attacker can also prevent transaction confirmations or mining by other miners, which can lead to network failures.
In the case of the PoS algorithm, to carry out a “51% attack,” one would need to possess more than half of the entire circulating coins of a cryptocurrency, which amounts to a substantial sum of money. Even if an attacker were to gather such a significant amount, the attack would become economically unreasonable.
3. Low Commissions
Commission fees often become an obstacle for miners. To some extent, mining using PoS systems is the best choice for many experts in mining new blocks in a distributed ledger network. The system validates transactions quickly, has low commission fees, and is easy to work with, allowing for high returns when mining new blocks in the blockchain network. Compared to the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus system, PoS offers very low costs for mining new blocks, which still depends on the blockchain network.
Disadvantages of Proof of Stake (PoS) Algorithm
Now let’s talk about the drawbacks of this consensus algorithm.
1. High Level of Centralization
These funds are usually held by a few people. For example, it is difficult to choose a price for an ICO that will attract the maximum number of buyers while ensuring that a large amount of funds does not fall into one person’s hands. As the currency accumulates, nodes gain a large amount of processing power in the network. Large owners can vote to decide further development of the network (as in NEO, etc.). This has a negative impact on the credibility of this consensus mechanism for many miners.
2. The “Nothing at Stake” Problem
The proof of work of participants is guaranteed by physical laws. If guilty, they cannot “break” the equipment and get back the electricity. This is a substantial penalty – they waste electricity and do not earn money. In Proof of Stake, the penalty exists only within the system: unethical players lose the deposits they froze. Once users withdraw, they are immune. This is the “nothing at stake” – the threat of creating a currency fork by removing his funds.
3. Limitation
To participate in the network as a validator, you must purchase a cryptocurrency, for which you must spend fiat currency – that is, you must invest in this business in some way. Sometimes the requirements of the network can be high and not everyone can afford it. On the other hand, the higher the ratio of validators, the greater the chance that they will be selected to verify a transaction block. However, there is always a chance in any case: some blocks are not checked by one person, but, for example, by a group of people simultaneously. Top validators purposefully buy tokens and consolidate them to earn as much money as possible.
Differences between PoS and PoW?
Proof of Work is a consensus that requires solving complex mathematical problems. Thus, miners are forced to use
very powerful, high-power-consuming equipment. The way Proof of Stake works is different. Mining is done by staking some currency from the wallet. The more they have, the greater the chance they have of becoming transaction validators, adding blocks to the network, and earning rewards. But there are other differences between the two consensus mechanisms.
Characteristics of PoW Consensus
The main task of miners is to solve complex mathematical problems to generate new hash values for the blocks to be connected. They are formed based on the hash value of the previous block, thus verifying the entire chain. Whoever solves the problem faster receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency.
Blockchains based on this consensus have serious vulnerabilities. If miners with a hash rate greater than 50% of the total network hash rate appear in the distributed ledger, they can control the blockchain. This is the 51% attack discussed above.
When using the consensus “proof of work,” miners receive income from adding new blocks. They also pay a portion of the commission charged when users make transactions on the platform.
Characteristics of PoS Consensus
When using “proof of ownership,” network nodes act as validators. The stake of money in their accounts is a pledge and guarantee of the existence of validators in the network and the correctness of their nodes.
First, nodes with more coins can attach a block and verify transactions. Before reaching a consensus between blocks, the currency in the user’s wallet is frozen. The entire process is automatic. Validators are paid for this activity.
Second, in PoS consensus, the risk of a “51% attack” still exists. However, for this, the “rogue” node must own at least 51% of all circulating coins. In other words, it makes no sense to do so. If someone wants to buy that many tokens, it will raise the rate. If the amount is reset, it will collapse.
Third, the system rewards verified transactions within the PoS consensus are paid for by the network. Verification is faster, and the network works more efficiently than its consistent “proof of work” counterpart.
Known blockchains using Proof of Stake consensus mechanism
Most post-Ethereum blockchains use the Proof of Stake consensus mechanism. Typically, each mechanism is modified according to the needs of the network. We will delve into them more below. Ethereum itself has now transitioned to Proof of Stake consensus with the Ethereum 2.0 update.
Ethereum
Ethereum is a general-purpose smart contract platform used to run decentralized applications. Its primary value is not its native Ether (ETH) but the opportunity provided by the EVM virtual machine.
Ether previously operated on the PoW algorithm, which required constantly solving complex mathematical problems. To do this, miners created huge farms with powerful computer equipment, consuming megawatts of electricity. With the transition to PoS, only money needs to be stored in an Ethereum wallet connected to the Internet to validate transactions. Mining farms are no longer needed, saving energy consumption equivalent to an entire country.
Polkadot
Polkadot is a network protocol based on PoS consensus algorithm that allows transferring any data between blockchains (not just tokens). This means that the network is a true multi-chain application environment where things like cross-chain registration and inter-chain computation are possible. Let’s simplify it: in the Ethereum network, the registration allocation only occurs between users within a given network (chain). In contrast, in Polkadot, information is stored on devices running across all integrated networks in the protocol.
Avalanche
Avalanche (AVAX) is an innovative smart contracts platform created by Ava Labs. It is a general-purpose blockchain prioritizing decentralization, security, and scalability while reducing costs and providing fast transactions.
The Avalanche network consists of three independent blockchains: X Chain, C Chain, and P Chain. Each chain has a separate purpose, which is different from the methods used by Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH), where all nodes check all transactions. The separation of these computing tasks provides Avalanche with higher throughput without sacrificing decentralization.
Solana
Solana is an innovative cryptocurrency system designed to support scalable decentralized applications (DApps). A key distinguishing feature of Solana is its Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus system supported by Tower Consensus. It is a variant of the Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) system, which allows distributed networks to reach consensus even in the presence of malicious nodes.
Tower Consensus reduces the computational power required for validating transactions by using this synchronous clock since it no longer needs to calculate timestamps of previous transactions. This helps Solana achieve throughput superior to most competitors.
Cardano
Cardano is a decentralized and scalable open-source distributed ledger platform based on Proof of Stake. It is one of the most stable, reliable, and mathematically verified blockchains of our era – running for over five years without interruption. The creation of Cardano was to perform similar tasks – such as launching smart contracts and creating DApps. In particular, the development and use of Proof of Stake (PoS) protocol elevate Cardano
smart contracts to a new level, offering high throughput and transaction speed, making DApps available to all participants, and addressing interoperability issues with the rest of the blockchain.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC)
Binance Smart Chain (BSC) is a smart contract blockchain network launched by the leading global cryptocurrency exchange Binance. It was officially launched in September 2020 with the aim of providing high-performance, low-cost decentralized finance (DeFi) services and an application development platform.
BSC is a blockchain network parallel to Binance Chain, adopting the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. Compared to Binance Chain, BSC has higher transaction throughput and lower transaction fees, while also providing smart contract functionality, enabling developers to build various decentralized applications (DApps) and digital assets.
Polygon
Polygon is an Ethereum scaling network aimed at addressing scalability, interoperability, and user experience issues on the Ethereum network. It was originally known as Matic Network before being rebranded as Polygon.
Polygon provides an efficient solution to achieve faster transaction speeds, lower transaction fees, and better user experience by adopting various technologies and layering structures.
Base
Base blockchain is a platform that provides efficient, secure, and transparent solutions for digital asset trading, offering users a decentralized trading environment through blockchain technology and ensuring the efficiency, security, and transparency of transactions.
Bottom Line
The development of distributed ledger technology has created an entire ecosystem composed of interconnected cryptographic trends, each evolving at an astonishing pace. PoS and PoW consensus algorithms are some of the most popular algorithms today, helping to systematize the mining process and will certainly make significant contributions to creating and developing new, more advanced consensus systems in the future, taking digital technology to a whole new level.