Overview of ZEROBASE: A Real-Time ZK Proof Network Backed by Binance Labs

The ZK (Zero-Knowledge) sector continues to attract significant venture capital investment. Recently, the real-time ZK proof network project, ZEROBASE, raised $5 million in funding from prominent investors including Binance Labs, Lightspeed Faction, Dao5, IDG, Matrix Partners, and Symbolic Capital. This marks the second notable financing in the ZK space since September, following a16z CSX’s lead investment in ZK proof generation layer developer Fermah.
The Appeal of ZEROBASE
In an increasingly crowded ZK landscape, the decision by cautious venture capitalists to invest in ZEROBASE raises questions. What sets this project apart?
Real-Time ZK Proof Network
ZEROBASE is designed to provide privacy and access to decentralized computing infrastructure. It was launched by Salus, a Web3 security company specializing in vulnerability research and security audits. Just three months prior, Salus received a grant from Ethereum, Aztec, Polygon, Scroll, Taikoxyz, and ZKsync for its work on zero-knowledge vulnerability analysis and security auditing.
Shawnc Chong, co-founder of ZEROBASE and Salus, hails from Malaysia and graduated from King’s College London. He has also invested in notable projects such as BounceBit and Sahara AI, showcasing his extensive experience in the crypto space.
The core aspects of ZK technology in blockchain revolve around two key features: privacy and scalability. ZK technology allows one party to verify information without exposing underlying data, making it an ideal choice for protecting sensitive information. Additionally, it enhances scalability by offloading complex computations off-chain while maintaining on-chain verification integrity.
Despite rapid advancements in ZK technology, various infrastructure challenges persist, including speed, cost, centralization, and scalability. ZEROBASE aims to address these challenges.
Features and Architectural Design
According to information from its website, ZEROBASE focuses on three main features:
- Rapid Proof Generation: ZEROBASE can generate ZK proofs within 400 milliseconds.
- Secure and Private Computation: It utilizes Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) for secure, private proof computations and tamper-proof data to ensure network security and privacy.
- Distributed Computing Architecture: The architecture eliminates single points of failure while maintaining decentralization, with consensus times of under one second.
In previous network designs, users interacted with a central hub to obtain a list of nodes, leading to issues with hub overload. If the hub encountered problems, the entire system was affected.
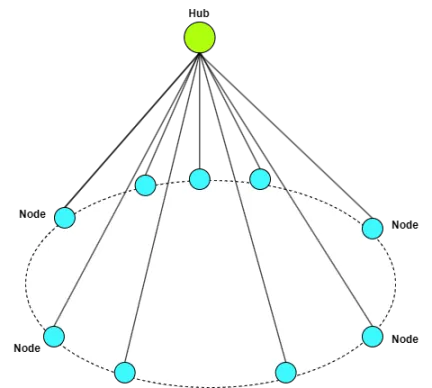
ZEROBASE implements a novel architecture that divides nodes into smaller subsets, each managed by its own hub. Each hub only maintains the status information of the nodes it oversees, allowing nodes to communicate directly with their respective hubs.
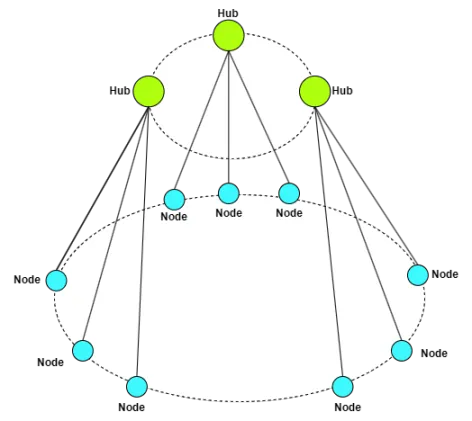
This design enables the system to scale smoothly by adding more hubs as the number of nodes increases.
The ZEROBASE Hub is responsible for broadcasting verification tasks. It distributes tasks across the ZEROBASE network, with proof generators randomly receiving proof generation assignments within specific time frames. The hub also handles user verification requests, requiring users to declare their tasks before broadcasting them on the network.
Additional functionalities of the ZEROBASE Hub include generating node connection credentials, processing data packets sent by nodes, and managing payment orders.
Future Prospects
Currently, ZEROBASE is seeing applications such as zkLogin, zkDarkPool, and Tiga Processor. With its innovative approach and strong backing, the future development of ZEROBASE is worth watching closely.