Solv Launches Staking Abstraction Layer (SAL) to Propel Bitcoin Staking into the Mainstream
The unique nature of the Bitcoin network and the complexities of Bitcoin staking pose significant challenges. To address this, Solv has introduced the Staking Abstraction Layer (SAL), aimed at enhancing the standardization and interoperability of Bitcoin staking, ultimately driving it toward widespread adoption.
SAL is built on a framework of smart contracts that facilitate seamless collaboration between stakers, Liquid Staking Token (LST) issuers, staking protocols, and other staking service providers. It simplifies user interactions with Bitcoin staking protocols, providing a streamlined staking experience.
Since focusing on Bitcoin staking in April 2024, Solv has enabled users to stake various Bitcoin assets, including BTCB, FBTC, and WBTC. As of September 30, 2024, over 20,000 BTC (valued at approximately $1.4 billion) have been staked through the Solv protocol, with more than 13,000 BTC coming from the BNB Chain. Ceffu serves as a validator, ensuring that all staked assets are securely and accurately deposited into protocols like Babylon and CoreDAO.
Why SAL Matters
With Bitcoin’s market cap exceeding $1.2 trillion, a staggering 99% of liquidity remains idle due to a lack of valuable use cases. Bitcoin staking represents a key solution to unlock significant liquidity, yet its current adoption rate lags far behind Ethereum’s 28%. If Bitcoin were to reach a similar staking rate, it could release approximately $330 billion in value, providing a major boost to the BTCFi sector.
However, Bitcoin staking faces developmental hurdles. The past six months have seen a rapid emergence of various Bitcoin staking protocols, such as Babylon and CoreDAO, each with different underlying technologies and asset security measures. This diversity complicates user selection and increases operational costs.
Moreover, because the Bitcoin mainnet does not support smart contracts, staking often requires cross-chain interactions, leading to complex user engagements across different networks. This not only raises the barrier to entry but also increases opacity and risk throughout the process.
How SAL Works
SAL aims to tackle these challenges by abstracting the technical differences and operational methods of various staking protocols, creating a standardized Bitcoin staking solution. Developers can leverage existing services within the SAL ecosystem to quickly implement Bitcoin staking, lowering the barrier to entry and fostering rapid innovation.
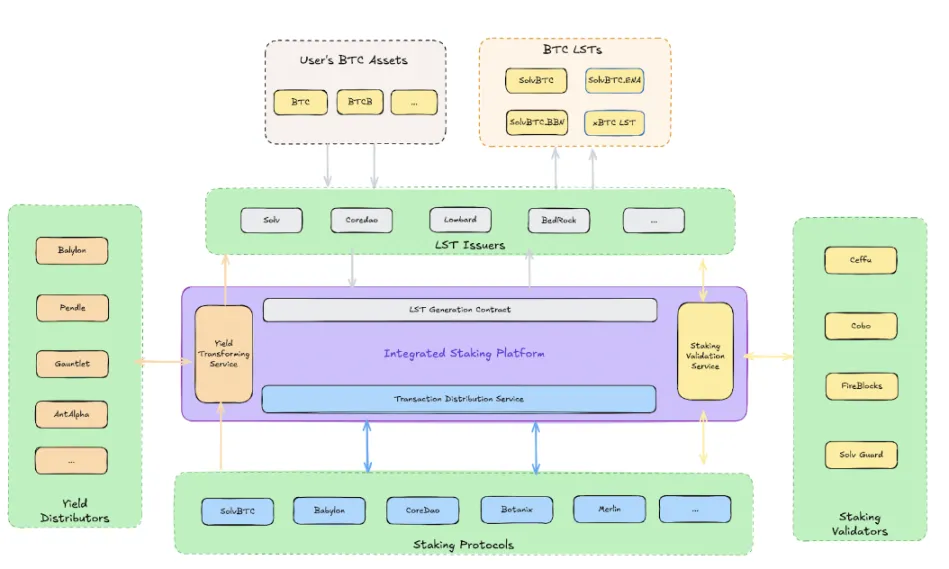
The Bitcoin staking ecosystem consists of four core roles:
- LST Issuers: Protocols that issue liquid staking tokens related to Bitcoin, bridging users and staking protocols. Examples include Solv and Lombard.
- Staking Protocols: Entities that accept Bitcoin assets and generate yields, such as Babylon and CoreDAO.
- Staking Validators: Responsible for verifying the integrity of the staking and transaction processes, ensuring LST issuers execute staking accurately. Notable validators include Ceffu and Fireblocks.
- Yield Distributors: Entities responsible for fairly and efficiently distributing staking rewards, such as Pendle and Antalpha.
SAL integrates these four roles effectively using smart contract technology and the Bitcoin mainnet.
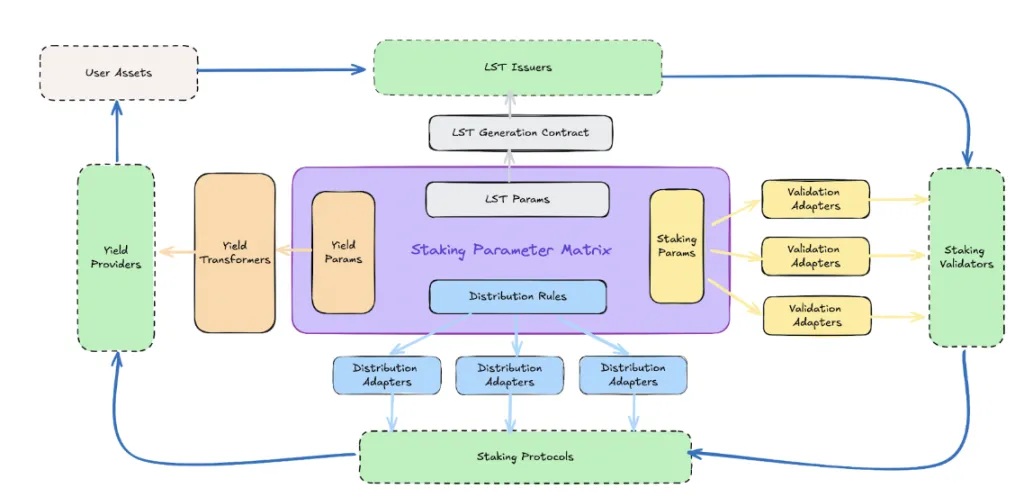
Core Components of SAL
SAL consists of five essential modules, including a core data model and several services:
- Staking Parameter Matrix (SPM): This core data model abstracts the parameters used across various staking processes, ensuring they are shared among SAL modules and participants.
- LST Generation Module: This module facilitates the issuance and redemption of BTC LST, managing interactions between the Bitcoin mainnet and EVM chains.
- Transaction Building Module: Responsible for creating staking transactions and estimating optimal fees, broadcasting these to the Bitcoin network.
- Validation Nodes: A set of algorithms on the Bitcoin mainnet that check the correctness of staking transactions as defined by the SPM.
- Yield Distribution Module: Calculates yield values and maps them to LST prices, also offering asset distribution solutions for users.
SAL: A Win-Win Solution
As the BTCFi narrative grows, Bitcoin staking is set to become a vital component of the Bitcoin ecosystem, requiring a secure, scalable solution. SAL offers a universal solution that meets the needs of all stakeholders.

For stakers, it provides a user-friendly experience while minimizing risks from operational errors and opaque protocols. Staking protocols benefit from reduced development costs and quicker liquidity access, allowing for ecosystem launch. LST issuers can enhance their protocol’s credibility and streamline development processes through collaboration within the SAL framework. Custodians also gain a new business model, effectively increasing revenue.
Current State of SAL
Several protocols and service providers have already joined the SAL ecosystem created by Solv. Babylon, CoreDAO, and GMX are among the first to adopt SAL, while Pendle has joined as a yield distribution protocol. Chainlink is using its CCIP technology to ensure cross-chain and asset transparency for LSTs generated via SAL. More protocols are expected to join in the coming months.

Conclusion
As Bitcoin staking continues to evolve, its impact on the blockchain ecosystem will grow. The demand from stakers seeking to maximize yield and developers pursuing innovation will unlock new on-chain opportunities. By enhancing the standardization and interoperability of the Bitcoin staking ecosystem, SAL promises tangible benefits for developers, users, and the entire Bitcoin community, paving the way for sustained growth and true mass adoption of Bitcoin staking.